BED BUGS
Want to learn more about BED BUGS?
The Queen of Clean is here to help you. Below is information we have compiled from our research.
> Start Here... Watch these informational videos by the Queen about BED BUGS...
Get BED BUG FINDERS - sold in set of 4 per package, 3 packs for savings! These last up to 90 DAYS, once opened.
Most people are concerned about bed bugs and believe that infestations around the world are increasing. Therefore, we've provided the following research and statistics from various sources to share with you.
Where people fear encountering Bed Bugs:
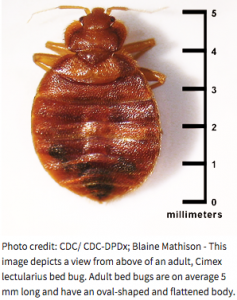
-
- 80% at hotels
- 52% on public transportation
- 49% in movie theaters
- 44% in retail stores
- 40% in medical facilities
- 36% in their own homes
- 32% places of employment and friends' homes
- 20% on a cruise ship or rental property
- The fear of getting bitten topped the list of concerns
- As the public's awareness of the bed bug resurgence grows, people are changing their behaviors to minimize the risk of an infestation:
- 27% have inspected or washed clothing upon returning from a trip
- 25% have checked a hotel room for bed bugs
- 17% have inspected or vacuumed a suitcase upon returning from a trip
- 12% have altered or canceled travel plans because of concern about bed bugs
How Many Bed Bugs Are There?

A lot!! One out of every 5 people, in the world, have had a bed bug infestation or know someone who has encountered bed bugs at home or in a hotel.
Using NPMA’s data (https://www.npma.org/),there's about a 10% infestation rate. Based on the 125.8 million households in the US, about 13 million households are potentially infested, not to mention the number of hotels that are infected.
Where Are the Bed Bugs?

- Anywhere In your home (Bed, sofa, laundry basket, walls, etc.)
- Hotels
- Airports
- Your car
- Transportation (Planes, buses, cabs, ride share)
- Movie theaters
- Concert venues
- Other people's homes
The Bed Bug Story
- According to some sources, we’ve been in a bed bug epidemic since 2010.
- Although most Americans are reputed to be aware of and concerned about
bed bugs, there’s little hue and cry over this epidemic. - Bed Bugs don’t trigger action by consumers until there’s visible evidence of an infestation e.g. bites, or a bed bug caught in a monitor, or a personal encounter with an influencer.
- There’s no quick fix for a bed bug infestation – it’s going to take time and money to control or eradicate it.
- The Environmental Protection Agency recommends an integrated pest management approach to controlling bed bugs that includes chemical and non-chemical techniques. See https://www.epa.gov/bedbugs/getting-rid-bed-bugs
What YOU Should Know about Bed Bugs
- Be concerned.
- Bed bugs are the most difficult pest to eradicate.
- Bed bugs are specialists in living next to people.
- They hide.
- They only come out to feed (when they’re hungry)
- They disperse (until the infestation becomes large)
- Despite their name, don’t focus on treating beds alone.
- Their favorite places are apartments/condominiums and single family homes.
- They really like hotels, too.
- Commercial treatments to eradicate or control bed bugs are expensive:
- Pesticide treatment for whole house: $500 - $700
- Heat treatment for one room: $800 - $1,000
- Professional heat treatment for the whole house: $2,000 and up
- The first line of defense is prevention – don’t bring them home.
- Early detection is the second line of defense – find them fast!
What YOU Should Do about Bed Bugs
- Be proactive!
- Stay vigilant!
- Follow the EPA’s bed bug prevention guidelines.
- Follow the Queen's inexpensive solution listed below.
Locate Bed Bugs using the Queen of Clean brand Bed Bug Finders™ CLICK HERE TO BUY NOW
-
- Spread them around the house, not just in beds
- They’re Inexpensive
- Easy to use
- They work!
Treat infestations with dry steam (suggestion: Vapamore MR-100 Prima for $299).
- Follow instruction and repeat as necessary.
- If you can’t get the results you want, get professional help.
Approach to Bed Bug Detection
Bed Bug Detection - WHAT SHOULD YOU DO?
- The best attractant for bed bugs is carbon dioxide.
- The second best attractant is heat.
- Carbon dioxide and heat are impractical for mass market bed bug detection devices. They are expensive, cumbersome or dangerous.
- Semiotic chemical-based devices are a practical and cost-effective compromise (See below).
The benefits of a Bed Bug device:
- Small
- Convenient
- Inexpensive
- Safe
- Effective
GET YOUR Bed Bug Finders NOW...
Watch this video to learn how to kill and treat Bed Bugs
Purchase a Vapamore steamer today!
Top 5 Bed Bug Signs
- You notice red stains or blood smears on sheets or pillowcases.
Unexplained bloodstains found on your light-colored sheets and pillowcases can be a result of bed bugs snacking on you and your family during the night. These rust colored stains may also be visible on furniture and clothing.
- You have red, itchy bites on your skin, sometimes in straight lines.
If you wake up with bug bites you don’t remember from the night before, or if the bites appear in a line, there is a good chance that you are dealing with a bed bug infestation. These bites are often very itchy.
- You see tiny white eggs or eggshells, smaller than a grain of sand.
Bed bug shells are a result of a boost in the bed bug population. These clear or white-colored shells are extremely small, but are tell-tale signs of an infestation. They are often found in the corners or crevices of mattresses, in side box springs, or in carpeting.
- You see spots that look like ground black pepper along seams and joints in your bedding.
These dark spots may be the fecal matter left behind by bed bugs. When wiped with a wet cloth, these dark spots will smear or stain. Mattress seams, bed corners, and box springs are where these stains tend to be spotted.
- You see live bugs or skins left behind from bed bugs molting.
If you suspect bed bugs you should investigate your mattress. Pull back the seams, and look for signs of infestation. While the egg and fecal matter is small, you will often see it in significant amounts, as well as live adult and juvenile bed bugs hiding in the nooks and crannies.

Where Bed Bugs May Be Hiding In Your Home
Surprise, surprise - bed bugs are more than likely found in your bed, under your mattress, atop the box spring, and along head and foot boards. However, they can also be found on other furniture, crawling along the walls, and scuttling across ceilings.
- Behind Pictures & Mirrors
- Behind Electrical Outlets
- Behind Headboards
- Inside Nightstands or Dressers
- Mattress Seams
- Along Baseboards
- Curtains or Drapes
- Upholstered Furniture
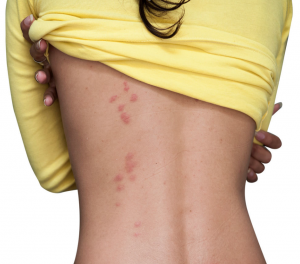
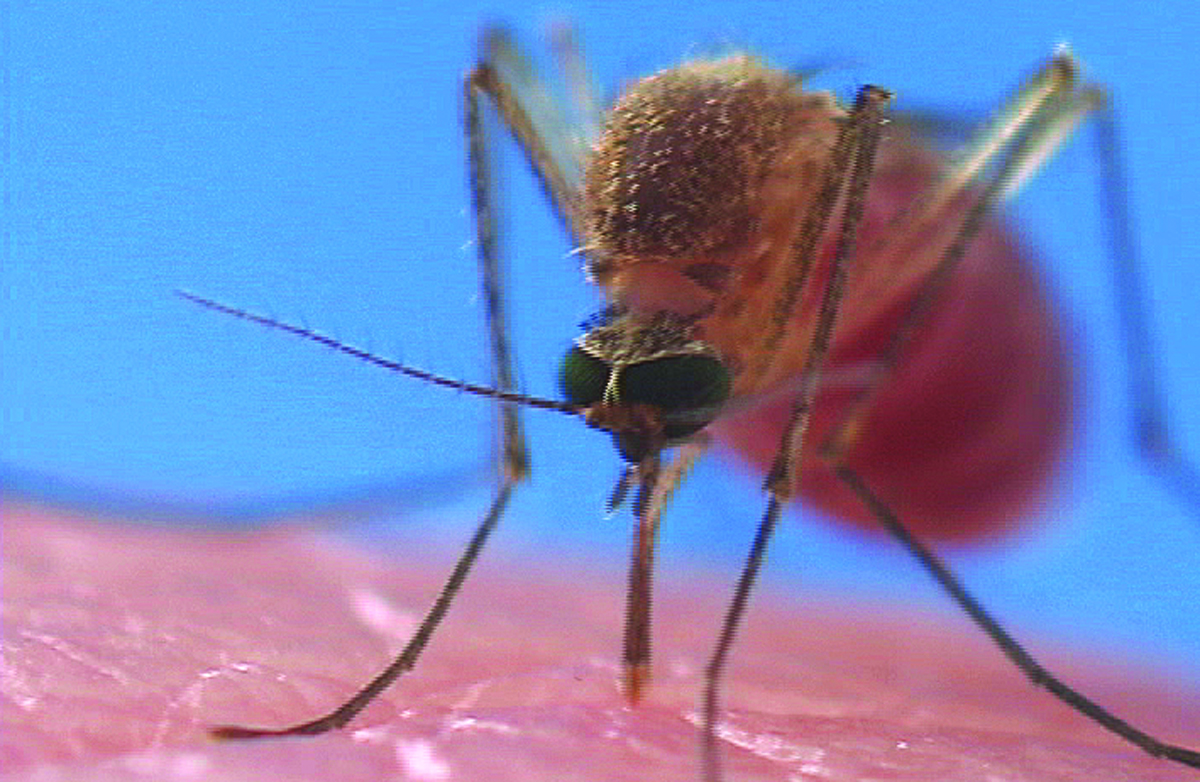
Dangers of Having Bed Bugs in Your Home
Unlike mosquitoes, which can transmit a host of diseases, bed bugs do not pose the same threat. However, bed bugs do leave nasty bites that can cause severe itching, which can lead to infection if left untreated.
Bed Bug Bite Vs. Mosquito Bite
GENERAL SYMPTOMS OF BITES
Mosquito Bites: Usually appears as puffy white and reddish bumps that begin a few minutes after the bite and become a reddish-brown bump a day or so after the bite. In some instances a host may have small blisters and dark spots that look like bruises in extreme cases.
Bed Bug Bites: Symptoms are variable and may result in no visible symptoms at first. However, symptoms of reddish bumps on skin, inflammation and red blotches that can become areas of raised, itchy bumps that eventually cause a burning sensation.
OTHER IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Sensitivity to Bites:
- Mosquito Bites: Generally, sensitivity to mosquito bites tends to decrease as the number of times someone is bitten increases. This may partially explain why children are usually more sensitive to mosquito bites than adults.
- Bed Bug Bites: Generally, the opposite relationship to number of bites and sensitivity occurs with bed bug bites. Often someone who is bitten by a bed bug doesn’t even realize the bug has fed, but as the number times they are bitten increases, the sensitivity to those bites also increases.
- Mosquito Bite Symptoms: Moderately painful, very irritating, itchy and leave round, red or pink mark on the skin. Mosquito bites may occur anytime during the day, at dusk or at night.
- Bed Bug Bite Symptoms: Usually are generally unnoticed and can be almost painless at the time of the bite. In fact, much of the time a person does not even realize they were bitten unless they notice the bite welts.
- Time to Heal: Mosquito bites usually clear up and “heal” much quicker than bed bug bites, which may persist for a few days or even longer.
Bite Sites:
- Mosquito bites are generally distributed in a random manner over parts of the body that are not protected by clothing (legs, face, back neck, etc.).
- Bed bug bites are more clustered and often occur in a distinct bite pattern that can be described as being multiple and arranged in a linear or circular fashion. Common locations include the neck, face, back, chest, arms, legs and around the crotch.
Signs & Characteristics
- In many instances a bed bug is unable to digest all of the blood meal it takes from a host, so it may actually excrete a portion of that blood meal onto the sheets the host is sleeping on. Therefore, if you see small, round bloodstains on your sheets, chances are good that a bed bug feed on you during the night.
- Hosts for both mosquitoes and bed bugs vary in attractiveness to the insects, which points out that both of these insects may bite one person and almost completely ignore someone else who is nearby. This behavior is very important to recognize since bed bugs are known to bite one person who is asleep and not bite another person who is asleep nearby.
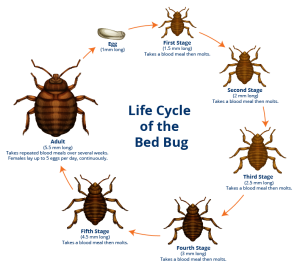
LIFE CYCLE DIFFERENCE
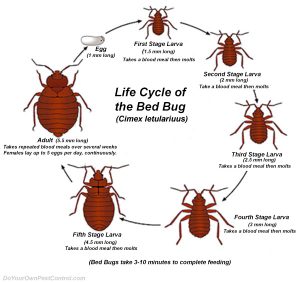
- Mosquitoes develop by complete metamorphosis, which means they go through four stages in their developmental cycle that is entirely different – egg, larvae, pupae and adults. Only the female mosquito adult bites and feeds on blood.
- Bed bugs develop by incomplete metamorphosis, which means they go through only three life stages – egg, nymphs and adults – and both the male and female nymphs and adults feed on blood.
DISEASE TRANSMISSION POTENTIAL
- Mosquitoes are known transmitters of many diseases that affect people or animals.
- Bed bugs are not proven transmitters of any known diseases to people or animals.
- If someone continues to scratch either mosquito or bed bug bites and does not keep the bite clean and medicated, there is a risk of a secondary infection.
SUMMARY
Should either mosquitoes or bed bugs become a pest issue, the best course of action is to contact your pest management professional. It is important to request an inspection, plus an integrated management plan that includes science-based information, recommendations, products and methods to be used.
Bed Bug Bites
Bed bugs feed on blood as their only source of nutrition. In order to mature into adults, they must feed once during each of their immature stages. Adult females also need blood in order to produce eggs. Although bedbugs do bite humans, they are not known to transmit diseases to people.
How to Identify the Bites
Blood spots found on one's sheets, bites and the presence of bed bug feces and cast skins are some of the indications of a bed bug infestation. Bites are commonly found on the parts of the body that are more likely to be exposed to bed bugs during sleep - the hands, neck, face, shoulders, legs and arms. While not always the case, bed bug bites are often grouped together in a small area and at times may occur in a line or a zigzag pattern. Bites normally look like small, flat or raised areas that may become inflamed, itchy, red or blistered. Bed bug bite reactions don’t always appear immediately after you’re bitten and may take a few days to begin causing symptoms. However, not everyone reacts to bed bug bites in the same manner.
The size of bed bug bites varies with a number of different factors. Bed bugs inject an anti-coagulant along with their saliva when they pierce the skin to take a blood meal. This anti-coagulant is mostly responsible for how a person reacts to the bite and determines the size of the bug’s bite. Since people will have various sensitivities to the bed bug’s bite, the size of the bite will vary, as well. Another factor that influences the size of a bed bug reaction is the number of times a person is bitten. Bite reactions of people bitten many times are also variable, and their response may be either more or less intense as the number of bites increases.
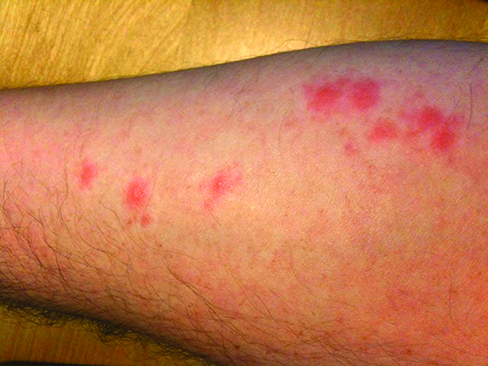
Bed bugs pierce human skin with elongated beaks through which they extract blood. Bed bug bites are not initially painful and can go unnoticed for hours or days. This allows bed bugs to withdraw human blood for up to 10 minutes with each feeding. Bed bug bites occur most commonly on exposed skin, such as the upper body, neck, arms and shoulders.
Bite Symptoms
Some individuals who are bitten by bed bugs develop itching, red welts or swelling the day after being bitten. However, bites may not become obvious for several days or at all on some individuals. Many people do not react at all to the bite of a bed bug—many bites leave no mark and go completely unnoticed.
Unlike those of other insects, bed bug bites may sometimes appear in tight lines of multiple, small, red marks where multiple bed bugs have fed along an exposed area. Bed bug bites can cause itchiness. Initially, a victim may detect a slight burning sensation. The burning area then develops red bumps, known as papules or wheals (rash). In extreme cases, bites may swell dramatically or turn into blister-like skin inflammations.
If you develop a rash after being bitten by a bed bug, avoid scratching the affected area. If the rash persists or becomes infected, contact a medical professional immediately.
Why Do They Bite?
Bed bugs are blood feeders that depend on blood for their food source, so they must consume blood for survival.
One bed bug will usually take more than one bite. Once a bed bug inserts its mouth parts and finds a suitable blood vessel, it will begin feeding. However, finding the right blood vessel may take more than one injection into the skin. In addition, bed bugs are very sensitive to movement by the host they are feeding on. Therefore, if a sleeping person moves, a feeding bed bug will probably withdraw its mouth parts and begin its search for a blood meal on another part of the body. It’s important to remember that the number of bites a person receives is not indicative of the number of bed bugs that feed on that person.
Risks Associated With Infections
Scratching bed bug bites and failure to keep the bites clean and disinfected may lead to a secondary infection that can cause further swelling and bleeding. Children, the elderly, and individuals with weak immune systems, particularly those who are bedridden, may develop secondary infections that result from bed bug bites.
How To Identify Bites On Pets
Bites on dogs and cats will look much like bites on people, and the pet owner may actually suspect a mosquito or flea bit the pet. As with people, bed bugs do not stay on pets, but return to a protected harborage site after feeding. In addition to bites, the presence of the bug’s feces, cast skins and the animal’s irritation at night are also indicators of bed bugs biting pets. Therefore, one of the best things to do is inspect the pet’s bedding and frequently groom the animal while being vigilant for the telltale signs of bed bug presence.
Most concentrated locations in the US for Bed Bugs
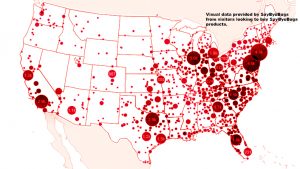
For more information on Bed Bugs, go to https://www.epa.gov/bedbugs/introduction-bed-bugs
...or check out: https://www.epa.gov/bedbugs/protecting-your-home-bed-bugs







